The system’s approach to management is a scenario that plays a very important role in creating coordinative relations between all related business systems.
“All organizations are perfectly designed to get the results they are now getting. If we want different results, we must change the way we do things.” – Tom Northup
The success ratio of any organization depends on the management approach taken. The company should function as a unit to achieve the set goals. One of the important theories related to management is the systems theory.
What is Systems Approach?
The systems approach to management is a concept which views a company as an interconnected purposive system that consists of several business sections. The entire system can be broken into three parts namely – input, process and output.
- Input involves the raw materials, funds, technology, etc.
- The process refers to activities related to management, technology, operations, etc.
- Output are the products, results, etc.
- The response or feedback in a system focuses on the information and data which is utilized for executing certain operations. These inputs aid in correcting the errors found in the processes.

It is a management approach which enables the leadership to see the company as a unified part or a major section of the larger outside corporate environment. Even a small activity in a section of a company has a substantial effect on other sections of the company. Such a system may be biological, physical or social, and may enable the management to efficiently determine the long-term goals of the company. The systems approach states that, for realizing the operations of an entity, it is essential to see the entity as a whole system.
Elements of a System
A system is made of different subsystems: internal and external. These subsystems are interconnected and influence each other and the system as a whole. Each of the subsystem interacts with the adjacent subsystem and they work in synergy for the betterment of the entire system. The limits within which the internal subsystems function, are determined by the system boundary. The external subsystems, on the other hand, are those which lie outside the boundary limits, but still influence the system.

For example: In a supermarket, the various subsystems are the marketing and advertising, sales, admin and finance department. These are the internal subsystems that lie within the boundary. The external subsystem here are the buyers or the customers who visit the store. Only when all these subsystems work together, the system is said to function effectively.
Open and Closed System
The organization can act as an open or a closed system. An open system is the one where the elements of the system can interact with the environment. This interaction can involve the transfer of material, information or manpower. The purchase department in any organization can be an example of open system. The buyers have to interact with suppliers (environment) and other internal departments to carry out the purchasing activity.
On the contrary, a closed system is the one which does not interact with the environment at all. There is no exchange of information, material or manpower between the system and environment. It is sometimes referred as an ‘isolated system’. An assembly line can be treated as a closed system if it does not interact for supply of raw materials. A research department can also be an example of closed system.
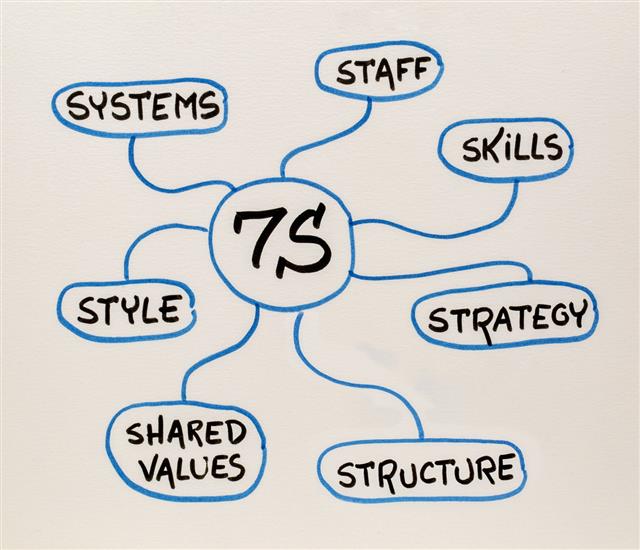
The 7S Model
This is a rough illustration of the 7S model that is developed by McKinsey & Company consulting firm. It exclusively concentrates on the seven key factors that are responsible for enabling organizations to reach their desired goals. Only when all these seven key areas work in a coordinated manner, will the company progress.
The key factors include:
♠ Organizational Strategy: The plan to maintain the competitive edge.
♠ Business Structure: The hierarchy of the organization.
♠ Efficient Systems: The day-to-day procedures and activities related to staff and processes.
♠ Style: The management style that is adopted.
♠ Skills: The competence of the employees.
♠ Staff: The employees of the organization.
♠ Corporate Shared Values: The core values on which the company is built. It also refers to the organization’s working culture.
All individual elements are highly dependent on each other, so a change in any one of them may disturb other sections. The company can analyze its current position and then look for areas where improvement is needed. For this, the organization can frame a set of questions based on the seven areas and look for answers for the same. Once, the lacking areas are identified, the right action can be taken.
The systems approach to management is the key to coordinate all the processes in a large company, and define the importance of individual procedures in the firm.